Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT)
Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT)
Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) medicine is a branch of healthcare dedicated to diagnosing and treating disorders related to the ear, nose, throat, head, and neck. ENT specialists, also known as otolaryngologists, manage conditions such as hearing loss, sinusitis, allergies, voice disorders, and head and neck cancers. They employ various diagnostic tools, including endoscopes and imaging studies, and offer treatments ranging from medications to surgical interventions.
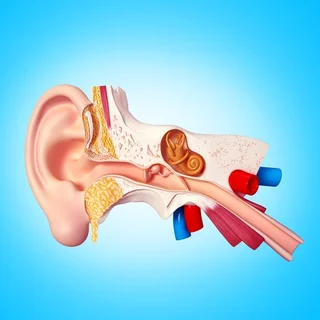
Tympanoplasty (Middle Ear Surgery)
Procedure Steps
- Anesthesia: The patient is given general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision behind the ear to access the tympanic membrane (eardrum).
- Graft placement: If the eardrum is perforated or damaged, the surgeon may repair it using a tissue graft from the patient's own body or a synthetic material.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures.
Benefits
Restoration of hearing: Tympanoplasty can improve hearing by repairing a perforated eardrum or restoring the function of the middle ear bones.
Prevention of middle ear infections: Repairing a perforated eardrum can help prevent recurrent middle ear infections.
Improved quality of life: Many patients experience improved quality of life after tympanoplasty, with relief from symptoms such as hearing loss, ear pain, and ear discharge.

Septoplasty (Nasal Septum Surgery)
Procedure Steps
- Anesthesia: The patient is given general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision inside the nose to access the nasal septum.
- Septum realignment: The surgeon straightens and repositions the deviated or displaced nasal septum.
- Closure: The incision is closed with dissolvable sutures, and nasal packing may be placed temporarily to support the septum.
Benefits
Improved nasal airflow: Septoplasty can correct nasal obstruction caused by a deviated septum, allowing for improved breathing.
Relief of nasal congestion: Many patients experience relief from symptoms such as nasal congestion, snoring, and sleep apnea after septoplasty.
Enhanced sinus drainage: Septoplasty may improve sinus drainage and reduce the risk of sinus infections.
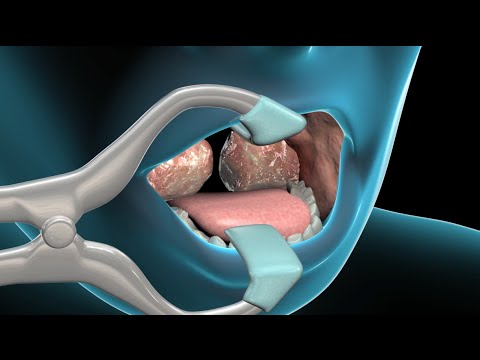
Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
Procedure Steps
- Anesthesia: The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Removal of tonsils and adenoids: The surgeon removes the tonsils (located at the back of the throat) and adenoids (located at the back of the nose) using surgical instruments or electrocautery.
- Hemostasis: Bleeding is controlled using pressure, cautery, or other techniques.
- Closure: The surgical sites are left to heal naturally without sutures.
Benefits
Reduction in throat infections: Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy can reduce the frequency and severity of throat infections, including tonsillitis and adenoiditis.
Improvement in breathing: Removal of enlarged tonsils and adenoids can improve airflow through the throat, reducing the risk of sleep-disordered breathing and obstructive sleep apnea.
Relief of symptoms: Many patients experience relief from symptoms such as sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and snoring after tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy.
Why Choose UniHealth for ENT Treatments?
1
Leadership in Otorhinolaryngology Care
UniHealth is a recognized leader in ENT surgery, offering a comprehensive range of surgical options and expertise.
2
Expert Otorhinolaryngologists
Our team consists of highly skilled ENT surgeons with extensive experience in treating ear, nose, and throat disorders and performing surgical interventions.
3
Personalized Approach
We provide individualized treatment plans, ongoing support, and multidisciplinary care to address the unique needs of each patient.
4
Innovation and Excellence
UniHealth is committed to advancing the field of ENT surgery through continuous research, education, and innovation.
